HyPURE® NX ZeroBrine Nanofiltration Process for PFAS Removal
November 2, 2022
What Are PFAS Compounds?
PFAS is a group of synthetic chemicals known as per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances. The hallmark of PFAS compounds is their series of carbon-fluorine bonds which form part of the “backbone” of these chemicals. The backbone is combined typically with a carboxylic acid or sulfonic acid functional group. There are some notable exceptions to this, such as Gen X compounds. The high energy required to break the carbon-fluorine bonds within PFAS substances means they are virtually indestructible, which made them ideal for a wide range of industrial uses. These products have been used in everything from firefighting foams and Teflon, to grease resistant coatings in carpets and chip packets.
The major challenge with these compounds is they do not break down in the environment, leading to bioaccumulation within animals and humans.
PFAS molecules are also highly mobile, due to their hydrophilic carboxylic acid and sulfonic acid functional groups enabling them to travel thousands of kilometres in groundwater and surface water. The combination of their ability to bioaccumulate and mobility has led to a global phase out of these products.
While PFAS compounds are not manufactured in Australia, they are still in use and are present in a range of imported consumer products. One of the primary sources of PFAS contamination is through firefighting foams. The sale and use of PFAS firefighting foams are banned in South Australia and New South Wales has introduced a range of restrictions in March last year (2021).
Due to its’ mobility and persistence PFAS contamination in the environment from firefighting foams, alongside other sources are widespread across Australia. The Current EPA national environmental management plant for PFAS recommends treatment of PFOS to 0.00023 µg/L (0.23 ng/L) and PFOA to 19 µg/L prior to environmental discharge.
Existing Treatment Methods
There are currently a wide range of treatment technologies used to remove PFAS species from surface and groundwater. Many of these solutions are generally only functional on small scale, or for treatment of highly concentrated waste due to the high energy requirements to operate at either extreme temperatures or pH ranges to breakdown C-F bonds.
Several proven methods of treatment exist, including activated carbon (GAC) and/or ion exchange (IX) adsorption and foam fractionation. These technologies have proven effective at PFAS removal when incoming concentrations are high, however reliability reduces, and operating costs increase at very low concentrations (1 – 5 ng/L). All technologies also struggle to remove short chain compounds such as PFBS.
Reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes provide the most complete removal of PFAS compounds, even at very low incoming concentrations (1 – 5 ng/L) however the management of waste brine creates a serious and currently unresolved challenge.
HyPURE® NX ZeroBrine nanofiltration process for PFAS removal
Hydroflux have developed a process which exploits the benefit of the physical barrier to PFAS compounds offered by nanofiltration membranes without the challenge of handling waste brine. The ZeroBrine process utilises our HyPURE® NX system fitted with NX Filtration direct hollow fibre nanofiltration membranes at its’ core.
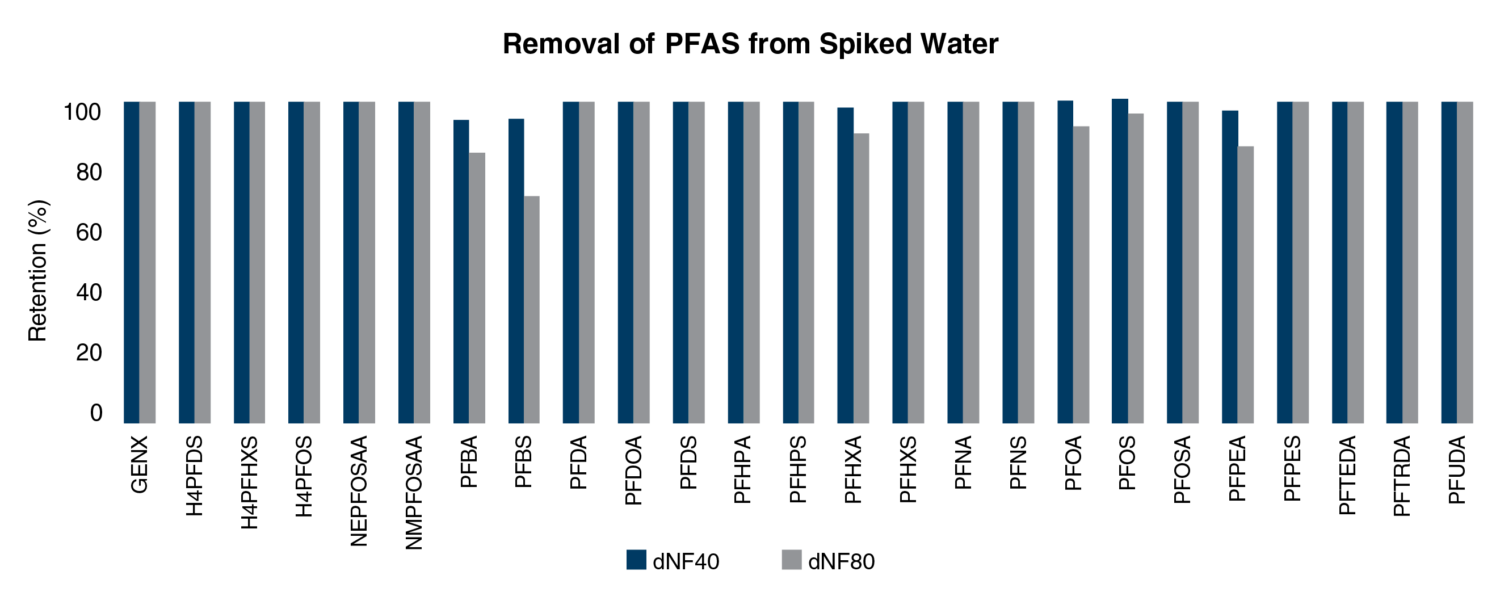
The NX Filtration dNF40 and dNF80 membranes have shown to be extremely effective at removal of PFAS compounds. The pore sizes and unique nanocoating within the membrane are ideally structured to retain PFAS and other organic pollutants whilst allowing dissolved inorganic salts to pass through.
The HyPURE NX ZeroBrine process can also be retrofitted to existing GAC, IX and foam fractionation systems to provide either improved treatment performance, reliability, and significant savings in operating costs (less media replacement).
The membrane provides an effective barrier to remove a wide range of PFAS compound. An example of typical removal rates for the dNF40 and dNF80 membranes are provided below.
Removal of Co-Contaminants
One of the major benefits of the HyPURE NX system is it removes a broad spectrum of other contaminants in a single process, meaning that additional targeted treatment systems do not need to be provided. An overview of some of the many compounds removed by the HyPURE NX system is provided below:
- Heavy Metals including Zn, Pb, Fe, Mn, Cu, Cd, Cr, As
- Chromium VI (< 1 µg/L ANZG 2018 95% SPL)
- Dissolved hydrocarbons
- Pathogens, viruses, bacteria
- Microplastics
HyPURE® NX provides municipal and industrial customers benefits previously not available from comparable membrane technology, to learn more please click here for municipal applications or click here for industrial applications.
About Hydroflux
The Hydroflux Group consist of eleven specialist companies which aim to deliver the highest level of engineering and scientific knowhow to the emerging issues of sustainability, climate adaptation and environmental protection with a specific focus on water and wastewater.
The Group employs over 100 staff and operates throughout Australia, New Zealand and the Pacific Islands with office locations in Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth, Auckland, Suva and Portsmouth.
Up Next
Reinforcing Our Position in The Green Energy Space
Categories
- Tradeshows
- Climate
- Community Engagement
- Corporate Announcements
- Group News
- Newsletters
- Product News
- Project Announcement


